用程序实现HTTP压缩和缓存 |
您所在的位置:网站首页 › js html代码压缩 › 用程序实现HTTP压缩和缓存 |
用程序实现HTTP压缩和缓存
|
用Asp.Net开发Web应用时,为了减少请求次数和流量,可以在IIS里配置gzip压缩以及开启客户端缓存。园子里已经有很多文章介绍了如何在IIS里开启压缩和缓存,但我想搞清楚该如何自己写代码来实现http压缩或者缓存,这样做的原因主要有下面两点: 1.IIS的版本不同,启用IIS的http压缩的方式也不同,IIS7还好一些,但对于IIS6来说,稍微麻烦一点; 2.如果我把应用部署在虚拟空间上,是没办法去设置虚拟主机的IIS的 所以了解如何用程序实现http压缩和缓存还是很有必要的。 实现压缩:在.net的System.IO.Compression命名空间里,有两个类可以帮助我们压缩response中的内容:DeflateStream和GZIPStream,分别实现了deflate和gzip压缩,可以利用这两个类来实现http压缩。 实现缓存:通过在response的header中加入ETag、Expires或LastModified,即可启用浏览器缓存。 下面我们创建一个小小的Asp.net Mvc2 App,然后逐步为它加入压缩和缓存。 首先新建一个Asp.net Mvc2的web application,建好后整个solution如下图: 实现缓存 要缓存的文件包括js、css、图片等静态文件。我在上面已经提到了,要使浏览器能够缓存这些文件,需要在response的header中加入相应的标记。要做到这一点,我们首先要使我们的程序可以控制到这些文件的response输出。用mvc的controller是一个不错的方法,所以首先在Global.asax.cs中加入下面的路由规则: public static void RegisterRoutes(RouteCollection routes){ routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}"); routes.MapRoute( "Default", // 路由名称 "{controller}/{action}/{id}", // 带有参数的 URL new { controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } // 参数默认值 ); routes.MapRoute( "Cache", // 路由名称 "Cache/{action}/{version}/{resourceName}", new { controller = "Cache", action = "Css", resourceName = "", version = "1" } // 参数默认值 );}上面加粗的代码增加了一条url路由规则,匹配以Cache开头的url,并且指定了Controller为Cache。参数action指定请求的是css还是js,resourceName指定请求的资源的文件名,version是css或js文件的版本。加入这个version参数的目的是为了刷新客户端的缓存,当css或js文件做了改动时,只需要在url中改变这个version值,客户端浏览器就会认为这是一个新的资源,从而请求服务器获取最新版本。 可能你会有疑问,加了这个路由规则之后,在View中引用css和js的方法是不是得变一下才行呢?没错,既然我要用程序控制js或css的输出,那么在View中引用js和css的方式也得做些改变。引用js和css的常规方法如下: 这种引用方式是不会匹配到我们新加的路由的,所以在View中,要改成如下的方式:
下面我们先实现这个CacheController。添加一个新的Controller,名为CacheController,并为它添加两个Action: using System.Web.Mvc;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class CacheController : Controller { public ActionResult Css(string resourceName, string version) { throw new System.NotImplementedException(); } public ActionResult Js(string resourceName, string version) { throw new System.NotImplementedException(); } }}
添加的两个Action为Css和Js,分别用于处理对css和js的请求。其实对css和对js请求的逻辑是差不多的,都是读取服务器上相应资源的文件内容,然后发送到客户端,不同的只是css和js文件所在的目录不同而已,所以我们添加一个类来处理对资源的请求。 在Controllers下添加一个类,名为ResourceHandler,代码如下: using System;using System.IO;using System.Web;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class ResourceHandler { private static readonly TimeSpan CacheDuration = TimeSpan.FromDays(30); private string _contentType; private string _resourcePath; private HttpContextBase _context; public ResourceHandler(string resourceName, string resourceType, HttpContextBase context) { ParseResource(resourceName, resourceType, context); } public string PhysicalResourcePath { get; private set; } public DateTime LastModifiedTime { get; private set; } private void ParseResource(string resourceName, string resourceType, HttpContextBase context) { if (resourceType.ToLower() == "css") { _contentType = @"text/css"; _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Content/{0}.css", resourceName); } if (resourceType.ToLower() == "js") { _contentType = @"text/javascript"; _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Scripts/{0}.js", resourceName); } _context = context; PhysicalResourcePath = context.Server.MapPath(_resourcePath); LastModifiedTime = File.GetLastWriteTime(PhysicalResourcePath); } public void ProcessRequest() { if (IsCachedOnBrowser()) return; byte[] bts = File.ReadAllBytes(PhysicalResourcePath); WriteBytes(bts); } protected bool IsCachedOnBrowser() { var ifModifiedSince = _context.Request.Headers["If-Modified-Since"]; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ifModifiedSince)) { var time = DateTime.Parse(ifModifiedSince); //加1秒的原因是request的header里的modified time没有精确到毫秒,而_lastModified是精确到毫秒的 if (time.AddSeconds(1) >= LastModifiedTime) { var response = _context.Response; response.ClearHeaders(); response.Cache.SetLastModified(LastModifiedTime); response.Status = "304 Not Modified"; response.AppendHeader("Content-Length", "0"); return true; } } return false; } private void WriteBytes(byte[] bytes) { var response = _context.Response; response.AppendHeader("Content-Length", bytes.Length.ToString()); response.ContentType = _contentType; response.Cache.SetCacheability(HttpCacheability.Public); response.Cache.SetExpires(DateTime.Now.Add(CacheDuration)); response.Cache.SetMaxAge(CacheDuration); response.Cache.SetLastModified(LastModifiedTime); response.OutputStream.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length); response.Flush(); } }}
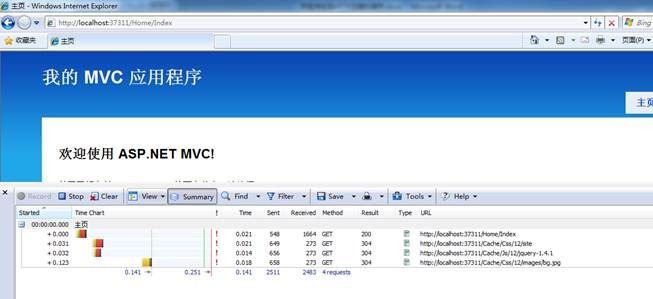
在上面的代码中,ProecesRequest负责处理对css和js的请求,先判断资源是否在客户端浏览器中缓存了,如果没有缓存,再读取css或js文件,并在header中加入和缓存相关的header,发送到客户端。 在这里有必要解释一下IsCachedOnBrowser这个方法。你可能会质疑这个方法是否有存在的必要:既然浏览器已经缓存了某个资源,那么在缓存过期之前,浏览器就不会再对服务器发出请求了,所以这个方法是不会被调用的。这个方法一旦被调用,那说明浏览器在重新请求服务器,再次读取资源文件不就行了吗,为什么还要判断一次呢? 其实,即使客户端缓存的资源没有过期,浏览器在某些时候也会重新请求服务器的,例如按F5刷新的时候。用户按了浏览器的刷新按钮之后,浏览器就会重新请求服务器,并利用LastModified或ETag来询问服务器资源是否已经改变,所以IsCachedOnBrowser这个方法就是用来处理这种情况的:读出Request中的If-Modified-Since,然后和资源的最后修改时间做比较,如果资源没被修改,则直接返回304的代码,告知浏览器只需要从缓存里取就行了。 下面在CacheController中使用这个ResourceHandler。先增加一个CacheResult的类,继承自ActionReult: using System;using System.Web.Mvc;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class CacheResult : ActionResult { private readonly string _resourceName; private readonly string _type; public CacheResult(string resourceName, string type) { _resourceName = resourceName; _type = type; } public override void ExecuteResult(ControllerContext context) { if (context == null) throw new ArgumentNullException("context"); var handler = new ResourceHandler(_resourceName, _type, context.HttpContext); handler.ProcessRequest(); } }}修改CacheController如下: using System.Web.Mvc;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class CacheController : Controller { public ActionResult Css(string resourceName, string version) { return new CacheResult(resourceName, "css"); } public ActionResult Js(string resourceName, string version) { return new CacheResult(resourceName, "js"); } }}可以看到,由于version只是用来改变url更新缓存的,对于我们处理资源的请求是没用的,所以我们在这两个Action中都忽略了这两个参数。 缓存的逻辑到这里就完成大部分了,下面我们为UrlHelper加两个扩展方法,方便我们在View中使用。增加一个UrlHelperExtensions的类,代码如下: using System.Web.Mvc;namespace MvcApplication1{ public static class UrlHelperExtensions { public static string CssCache(this UrlHelper helper, string fileName) { return helper.Cache("Css", fileName); } public static string JsCache(this UrlHelper helper, string fileName) { return helper.Cache("Js", fileName); } private static string Cache(this UrlHelper helper, string resourceType, string resourceName) { var version = System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ResourceVersion"]; var action = helper.Action(resourceType, "Cache"); return string.Format("{0}/{1}/{2}", action, version, resourceName); } }}version配置在web.config的appSettings节点下。然后修改Site.Master中对css和js的引用: 这样,缓存基本上算是完成了,但我们还漏了一个很重要的问题,那就是css中对图片的引用。假设在site.css中有下面一段css: body{ background-image:url(images/bg.jpg);}然后再访问~/Home/Index时就会有一个404的错误,如下图:
由于css中对图片的链接采用的是相对路径,所以浏览器自动计算出http://localhost:37311/Cache/Css/12/images/bg.jpg这个路径,但服务器上并不存在这个文件,所以就有了404的错误。解决这个问题的方法是再加一个路由规则: routes.MapRoute( "CacheCssImage", // 路由名称 "Cache/Css/{version}/images/{resourceName}", new { controller = "Cache", action = "CssImage", resourceName = "", version = "1", image = "" } // 参数默认值 );这样就把对~/Cache/Css/12/images/bg.jpg的请求路由到了CacheController的CssImage这个Action上。下面我们为CacheController加上CssImage这个Action: using System.Web.Mvc;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class CacheController : Controller { public ActionResult Css(string resourceName, string version) { return new CacheResult(resourceName, "css"); } public ActionResult Js(string resourceName, string version) { return new CacheResult(resourceName, "js"); } public ActionResult CssImage(string resourceName, string version) { return new CacheResult(resourceName, "image"); } }}然后修改ResourceHandler类,让他支持image资源的处理如下: using System;using System.IO;using System.Web;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class ResourceHandler { ... private void ParseResource(string resourceName, string resourceType, HttpContextBase context) { if (resourceType.ToLower() == "css") { _contentType = @"text/css"; _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Content/{0}.css", resourceName); } if (resourceType.ToLower() == "js") { _contentType = @"text/javascript"; _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Scripts/{0}.js", resourceName); } if (resourceType.ToLower() == "image") { string ext = Path.GetExtension(resourceName); if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(ext)) { ext = ".jpg"; } _contentType = string.Format("image/{0}", ext.Substring(1)); _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Content/images/{0}", resourceName); } ... } ... }}再次访问~/Home/Index,可以看到css中的image已经正常了:
到这里,缓存的实现可以说已经完成了,但总觉得还有个问题很纠结,那就是在修改css或js之后,如何更新缓存?上面的代码中,可以修改web.config中的一个配置来改变version值,从而达到更新缓存的目的,但这是一个全局的配置,改变这个配置后,所有的css和js的url都会跟着变。这意味着即使我们只改动其中一个css文件,所有的资源文件的缓存都失效了,因为url都变了。为了改进这一点,我们需要修改version的取值方式,让他不再读取web.config中的配置,而是以资源的最后修改时间作为version值,这样一旦某个资源文件的最后修改时间变了,该资源的缓存也就跟着失效了,但并不影响其他资源的缓存。修改UrlHelperExtensions的Cache方法如下: private static string Cache(this UrlHelper helper, string resourceType, string resourceName) { //var version = System.Configuration.ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ResourceVersion"]; var handler = new ResourceHandler(resourceName, resourceType, helper.RequestContext.HttpContext); var version = handler.LastModifiedTime.Ticks; var action = helper.Action(resourceType, "Cache"); return string.Format("{0}/{1}/{2}", action, version, resourceName); }实现HTTP压缩 在文章的开头已经提到,DeflateStream和GZIPStream可以帮助我们实现Http压缩。让我们来看一下如何使用这两类。 首先要清楚的是我们要压缩的是文本内容,例如css、js以及View(aspx),图片不需要压缩。 为了压缩css和js,需要修改ResourceHandler类: using System;using System.IO;using System.IO.Compression;using System.Web;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class ResourceHandler { private static readonly TimeSpan CacheDuration = TimeSpan.FromDays(30); private string _contentType; private string _resourcePath; private HttpContextBase _context; private bool _needCompressed = true; public ResourceHandler(string resourceName, string resourceType, HttpContextBase context) { ParseResource(resourceName, resourceType, context); } public string PhysicalResourcePath { get; private set; } public DateTime LastModifiedTime { get; private set; } private void ParseResource(string resourceName, string resourceType, HttpContextBase context) { if (resourceType.ToLower() == "css") { _contentType = @"text/css"; _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Content/{0}.css", resourceName); } if (resourceType.ToLower() == "js") { _contentType = @"text/javascript"; _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Scripts/{0}.js", resourceName); } if (resourceType.ToLower() == "image") { string ext = Path.GetExtension(resourceName); if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(ext)) { ext = ".jpg"; } _contentType = string.Format("image/{0}", ext.Substring(1)); _resourcePath = string.Format("~/Content/images/{0}", resourceName); _needCompressed = false; } _context = context; PhysicalResourcePath = context.Server.MapPath(_resourcePath); LastModifiedTime = File.GetLastWriteTime(PhysicalResourcePath); } public void ProcessRequest() { if (IsCachedOnBrowser()) return; byte[] bts = File.ReadAllBytes(PhysicalResourcePath); WriteBytes(bts); } public static bool CanGZip(HttpRequestBase request) { string acceptEncoding = request.Headers["Accept-Encoding"]; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(acceptEncoding) && (acceptEncoding.Contains("gzip"))) return true; return false; } protected bool IsCachedOnBrowser() { var ifModifiedSince = _context.Request.Headers["If-Modified-Since"]; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(ifModifiedSince)) { var time = DateTime.Parse(ifModifiedSince); //加1秒的原因是request的header里的modified time没有精确到毫秒,而_lastModified是精确到毫秒的 if (time.AddSeconds(1) >= LastModifiedTime) { var response = _context.Response; response.ClearHeaders(); response.Cache.SetLastModified(LastModifiedTime); response.Status = "304 Not Modified"; response.AppendHeader("Content-Length", "0"); return true; } } return false; } private void WriteBytes(byte[] bytes) { var response = _context.Response; var needCompressed = CanGZip(_context.Request) && _needCompressed; if (needCompressed) { response.AppendHeader("Content-Encoding", "gzip"); using (var stream = new MemoryStream()) { using (var writer = new GZipStream(stream, CompressionMode.Compress)) { writer.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length); } bytes = stream.ToArray(); } } response.AppendHeader("Content-Length", bytes.Length.ToString()); response.ContentType = _contentType; response.Cache.SetCacheability(HttpCacheability.Public); response.Cache.SetExpires(DateTime.Now.Add(CacheDuration)); response.Cache.SetMaxAge(CacheDuration); response.Cache.SetLastModified(LastModifiedTime); response.OutputStream.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length); response.Flush(); } }}
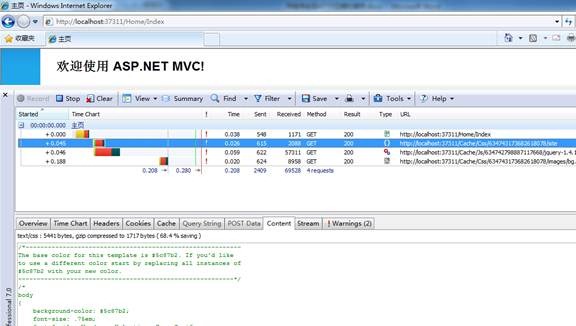
加粗的代码是修改的内容,并且只用了gzip压缩,并没有用deflate压缩,有兴趣的同学可以改一改。 为了压缩View(aspx),我们需要添加一个ActionFilter,代码如下: using System.IO.Compression;using System.Web;using System.Web.Mvc;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ public class CompressFilterAttribute : ActionFilterAttribute { public override void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext) { var response = filterContext.HttpContext.Response; HttpRequestBase request = filterContext.HttpContext.Request; if (!ResourceHandler.CanGZip(request)) return; response.AppendHeader("Content-encoding", "gzip"); response.Filter = new GZipStream(response.Filter, CompressionMode.Compress); } }}然后为HomeController添加这个Filter: using System.Web.Mvc;namespace MvcApplication1.Controllers{ [HandleError] [CompressFilterAttribute] public class HomeController : Controller { public ActionResult Index() { ViewData["Message"] = "欢迎使用 ASP.NET MVC!"; return View(); } public ActionResult About() { return View(); } }}这样就可以压缩View了。 最终的效果如下图: 第一次访问:
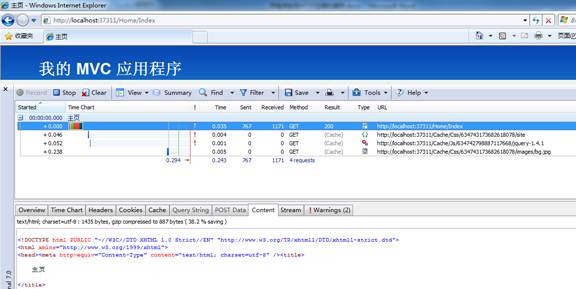
第二次访问:
|
【本文地址】